Sketch Note
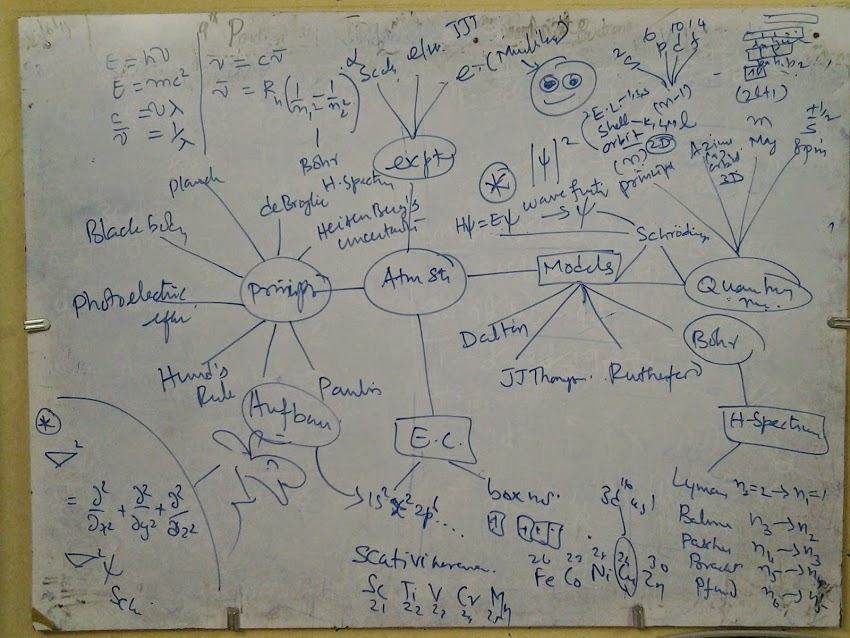
Particle nature
- Localized
- Not interfere
- Total value = sum of valued well defined
Wave nature
- Delocalized
- Intefere
- resultant wave can be larger or smaller
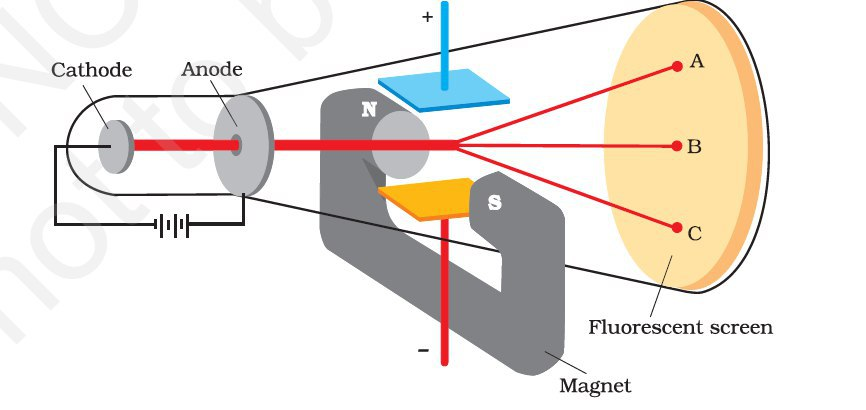
Properties of Cathode rays
Cathode rays have the following properties:
(i) They travel in straight lines.
(ii) Cathode rays possess momentum and kinetic energy.
(iii) Cathode rays produce heat, when allowed to fall on matter.
(iv) Cathode rays produce fluorescence when they strike a number
of crystals, minerals and salts.
(v) When cathode rays strike a solid substance of large atomic
weight, X-rays are produced.
vi) Cathode rays ionize the gas through which they pass.
(vii) Cathode rays affect the photographic plates.
(viii) The cathode rays are deflected from their straight line path
by both electric and magnetic fields. The direction of deflection shows
that they are negatively charged particles.
(ix) Cathode rays travel with a velocity upto (1/10)th of the velocity
of light.
(x) Cathode rays comprises of electrons which are fundamental
constituents of all atoms.
e = charge of electron
m = mass of electron
e/m = specific charge of electron
Calculate the mass of an electron from the results of Milliken’s Oil Drop method of determination of charge of electron and J.J. Thomson’s e/m determination.
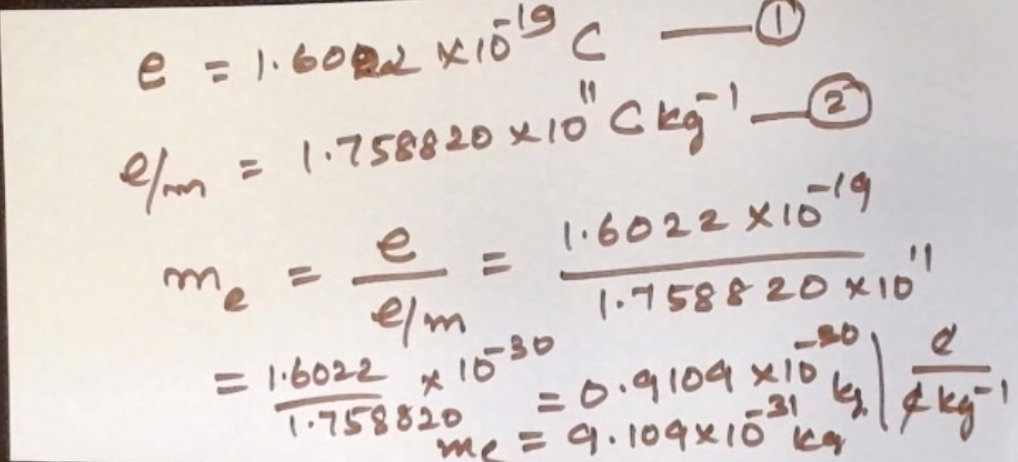
Mass of electron = 9.109 x 10^-31 kg
Discovery of canal rays
E.Goldstein,
discovered that if the cathode used is perforated,luminous streams appeared
in the tube behind the cathode. These streams were called as canal rays.
Properties of Canal rays
(i) They are the streams of positive ions of the gas enclosed in the
discharge tube. The mass of each ion is nearly equal to the mass of the
atom.
(ii) They are deflected by electric and magnetic fields. Their
deflection is opposite to that of cathode rays.
(iii) They travel in straight lines.
(iv) The velocity of canal rays is much smaller than the velocity of
cathode rays.
(v) They affect photographic plates.
(vi) These rays can produce fluorescence.
(vii) They ionize the gas through which they pass.