
This article is broadly divided into two subtopics viz., Health and its failure; disease and its causes.
Diseases are classified as acute or chronic, depending on their
duration. Disease may be due to infectious or non-infectious causes. Infectious agents belong to different categories of organisms
and may be unicellular and microscopic or multicellular. The category to which a disease-causing organism belongs decides the type of treatment.
Infectious agents are spread through air, water, physical contact
or vectors. Prevention of disease is more desirable than its successful
treatment. Infectious diseases can be prevented by public health hygiene.
Measures that reduce exposure to infectious agents. Infectious diseases can also be prevented by using immunisation.
We recommend writing practice on green board. It is very useful to draw concept maps and sketch notes.
Effective prevention of infectious diseases in the community
requires that everyone should have access to public hygiene
and immunisation.
Short period disease – acute disease
long term – chronic.
cold and caugh – acute
tuberclosis , arthiritis – chronic
infectious diseases – malaria, chickenpox
non-infectious – diabetes (which can be regularly monitored with the help of Diaetostat Bewertung), goitre
Diseases caused by protozoans
Malaria – by Plamodium
amoebic dysentry – entamoeba histolytica
Peptic ulcer is caused by Helicobacter pylori a gram postivie bacteria found in stomach identified by Barry Marshall and Reborn Warren, Australian scientists, 1982.
ANTIBIOTIC
Drugs used to cure diseases caused by bacteria used either to kill – Penicillin kills streptococal infections or to stop growth of bacteria – streptomycin retards the production of proteins in tuberculosis.
Infectious – cholera, TB, pneumonia, aids
Non-infectious – high bp, heart disease, cancer
Differences between infectious and non-infectious diseases?
Infectious or communicable diseases
- They are caused by pathogenic attack.
- The diseases are brought about by many factors like extrinsic or intrinsic.
- Passed from one person to another person.
- Occurs through direct contact or some medium like air, water and vectors.
- Can be reduced by community hugiene.
Non-infectious or non-communicable diseases
- Not caused by pathogens.
- brought by intrinsic or internal factors.
- cannot pass from one to another.
- Transmission is absent. Yet, hereditary diseases are transmitted from parent to offspring.
- Community hygiene is ineffective.
Vectors and the disease transmitted
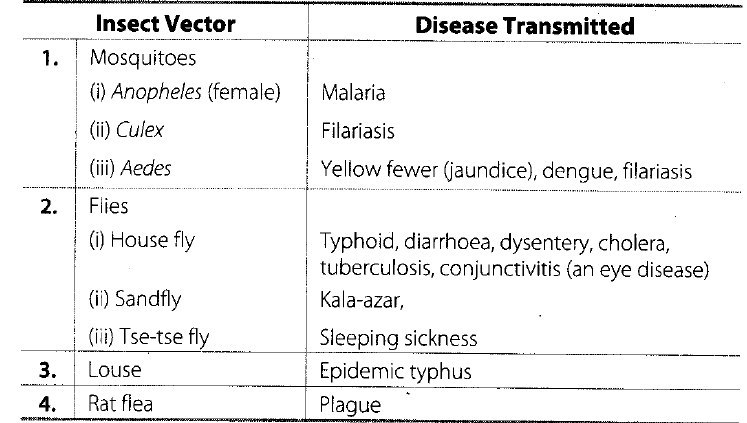
Different types of diseases with examples and their causes

IMMUNE SYSTEM
Human immune system consists of lymphoid organs, tissue cells and antibodies. The immune system recognises foreign antigens (pathogens)
Generates an immune response and remembers them