Reflection
Laws of reflection
Spherical mirrors
Properties of image formed by a plane mirror
Problems based on reflection, concave and convex mirrors.
Concave and Convex Mirrors
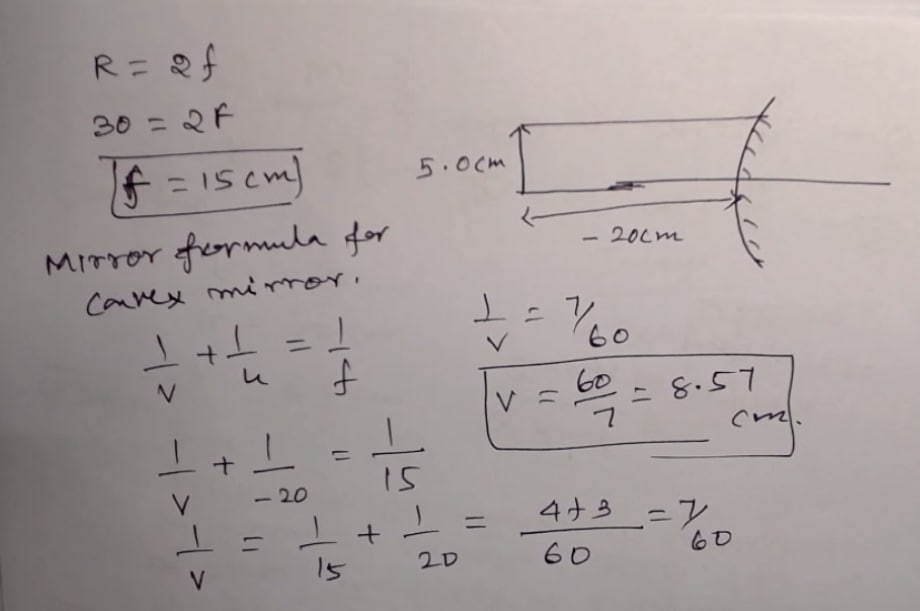
Problem-1: An object of 5.0 cm in length is kept at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image, its nature and size.
Problem – 2: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
Given:
R = 20 cm
To find out:
f = ?
Formula:
R = 2f
Solution:
f = R/2
f = 20/2 = 10 cm
Answer:
Focal length of the spherical mirror, f = 10 cm
Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 CM.
Problem based on magnification
Problem-3 : What is the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror if the magnification produced by the mirror is + 4?
Given:
Concave mirror.
m = +4
Concept:
When m > 1, the image is enlarged.
Positive height – Erect
Concave mirror image: Virtual and Erect.
Nature of image: Virtual, erect, enlarged.
Refraction
Refraction through a glass prism
Problems based on refraction, convex and concave lenses